Yavapai Regional Medical Center West
1003 Willow Creek Road
Prescott, AZ 86301
928.445.2700
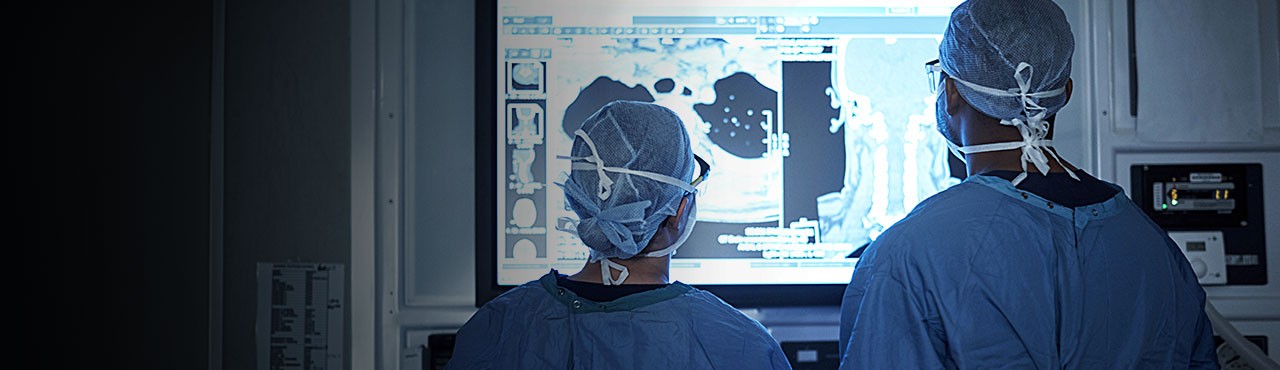
Yavapai Regional Medical Center (YRMC) Imaging Services combines an exceptional team –radiologists, radiologic technologists and registered nurses – with an extensive menu of advanced imaging technologies. Armed with sophisticated technology, our Imaging Services team strives to provide patients of all ages:
YRMC performs more than 120,000 diagnostic imaging procedures each year at YRMC East and YRMC West. Our imaging procedures include:
Our excellent interventional radiology team uses diagnostic angiography to detect abnormalities or blockages in the blood vessels. These interventional radiologists study blood vessels by:
Angioplasty helps improve blood flow in the body’s arteries and veins. Our interventional radiologists use imaging techniques to guide a catheter – a thin plastic tube – into an artery or vein in order to open the blocked vessel. During angioplasty, a small wire mesh tube called a stent may be permanently placed in the newly opened artery or vein to help it stay open.
During these kinds of biopsies, radiologists collect tissue from a specific area of the body – breast, lungs, liver, thyroid – for pathological evaluation. The patient rests in the CT-scanner and the images it produces helps the physician determine the exact position within the targeted tissue.
Computed tomography (CT scan) is a type of x-ray that produces cross-sectional images that provide your physician detailed images to help with diagnosis. The images generated during a CT scan can be reformatted in multiple planes and three-dimensional images. CT images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels can provide greater detail than traditional x-rays.
CT angiography combines a computerized tomography (CT) scan with an injection of contrast material (a special dye) to create images of blood vessels and tissues. The contrast material is injected through an intravenous (IV) line started in the arm or hand. While the contrast material flows through the blood vessels to the various organs, a CT scan is performed. A special computer is used to process and view the images in different planes and projections. CT angiography can help your physician diagnosis a range of conditions including aneurysms, blood clots, injuries and more.
Fluoroscopy permits physicians to exam either the large bowel or the upper gastrointestinal tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach and the first small portion of the bowel or intestine. A fluoroscope is an x-ray unit combined with a television screen that allows a radiologist to observe the flow of a compound called liquid barium through the part of the body being examined.
This imaging study allows radiologists to locate and monitor hard-to-find neuroendocrine tumors. First, Gallium-68 dotatate – a radiopharmaceutical tracer used to detect certain diseases – is administered to the patient by IV. After, the patient undergoes a PET scan to pinpoint the tumor’s location and monitor its response to treatment. Galium-68 dotatate is a mild agent so it doesn’t cause reactions like nausea or fatigue.
To learn more about important interventional heart studies performed by YRMC interventional radiologists, visit the James Family Heart Center.
Interventional radiology procedures are minimally invasive. They’re used to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions such as arterial blockages, tumors and blood clots. Radiologists use small instruments, imaging technology and computers to perform these procedures. Interventional radiology procedures help prevent some surgical procedures and allow quick recovery for patients.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic technique that uses a magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to generate detailed and cross-sectional images of the body. Because it produces better soft-tissue images than x-rays, MRI is most commonly used to create sharp images of the brain, spine, thorax, vascular system, prostate and musculoskeletal system (areas like the knee and the shoulder). MRI is safe and noninvasive and produces no x-ray radiation, although it is not typically recommended for pregnant women.
Digital mammography uses solid-state detectors – much like those in digital cameras – to convert x-rays into an electronic image of the breast that can be seen on a computer screen. More information about breast health and breast care is available at our BreastCare Center. Please note that mammography screening is not available through the Imaging Services Department at YRMC West in Prescott. It is available on the campus of YRMC West through Prescott Medical Imaging and through the BreastCare Center in Prescott Valley.
This exam is used to determine if someone is swallowing safely and effectively as well as to observe the function or structure of the esophagus to the stomach. While the patient swallows barium liquids and food, the radiologist uses a video x-ray called fluoroscopy to view the process real-time and to take images.
During this diagnostic procedure, a radiologist uses contrast and fluoroscopy to detect problems in the spinal canal, including the spinal cord, nerve roots, and other tissues. The contrast – injected into the spinal column before the procedure – allows the radiologist to produce more detailed images of the body than standard x-rays. Sometimes this procedure is combined with a CT scan to better visualize the spine and surrounding tissues.
Nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive material – called radiotracers – to diagnose illness and to determine the severity of an illness. After the radiotracer is injected into a patient, it accumulates in the organ or part of the body that is being examined. A special camera detects radioactive emissions and then takes images of the area. These pictures provide information that physicians use to make a diagnosis.
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a nuclear medicine imaging exam that helps doctors evaluate how well organs and tissues are functioning. Depending on the type of nuclear medicine exam, a small amount of radioactive material – called a radiopharmaceutical – is injected into the body. The radiopharmaceutical eventually accumulates in the part of the body that is being examined. An imaging device detects the emissions from the radiopharmaceutical and produces pictures as well as provides other information. PET scans can detect cancer, determine blood flow to the heart, and evaluate brain abnormalities.
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves – not radiation – to produce images of the body’s organs, vessels and tissues. During an ultrasound exam, inaudible sound waves create “echoes” as they bounce off organs and tissue. These echoes are then converted into an image on a computer screen. Ultrasound may be used to:
Ultrasound-guided biopsies are used to extract fluid, cells or tissue from many areas of the body, including the breast, liver and thyroid. A small amount of gel is placed on the patient’s skin. The radiologist then uses a hand-held device (transducer) that allows sound waves to travel between the body and the transducer. This produces images on a screen that the radiologist views to detect the specific area to be biopsied.
Vascular ultrasound tests are non-invasive, safe and painless procedures that do not use radiation to locate blocked vessels and other conditions. During a vascular ultrasound a radiologic technologist places ultrasound gel directly on the skin. A small transducer transmits sound waves into the body. The transducer collects the sounds as it bounces back and a computer uses those sound waves to create images.
Some children have an abnormality called VU reflux which causes urine in the valve or ureter to flow backwards. These children may need a bladder and lower urinary tract exam called voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG). Fluoroscopy and a small amount of contrast material are used to produce images of the urinary system, allowing the radiologist to see the child’s bladder and lower urinary tract as it functions and then to make a diagnosis.
YRMC’s Imaging Services team understands that you will have questions about any medical exam your child needs to undergo. Our team is available to explain the procedure your physician has recommended for your child. Please visit FAQs for more information.
X-rays are the oldest and most frequently used medical imaging procedure. X-rays help physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. X-rays expose a part of the body to a small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of the inside of the body.
Our Imaging Services team is proud to be accredited by the American College of Radiology (ACR). ACR accreditation requires peer review by board-certified radiologists and medical physicists who are experts in this area. This knowledgeable team evaluates our:
In addition to ACR accreditation we demonstrate our commitment to excellence by participating in the Image Gently® and Image Wisely® radiation safety initiatives.
YRMC Imaging Services serves both inpatients (people who are in the hospital) and outpatients (people who come to the hospital for a specific service, but are not hospital patients). Our outpatients – like our hospitalized patients – have nursing and other medical professionals available to them should they need it during their Imaging Services exam.


1003 Willow Creek Road
Prescott, AZ 86301
928.445.2700

7700 East Florentine Road
Prescott Valley, AZ 86314
928.445.2700

7700 East Florentine Road
Prescott Valley, AZ 86314
928.771.7577

810 Whipple Street
Prescott, AZ 86301
928.771.7577

7700 East Florentine Road
Building B, Suite 105
Prescott Valley, AZ 86314
928.771.7577
YRMC East – Imaging Services
7700 East Florentine Road
Prescott Valley, AZ 86314
928.771.7577
Monday – Friday: 7:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m.
Saturday by appointment only
YRMC West – Imaging Services
1003 Willow Creek Road
Prescott, Arizona 86301
928.771.7577
Monday – Friday: 7:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m.
Dignity Health Imaging Center, Prescott
810 Whipple Street
Prescott, AZ 86301
928.771.7577
Monday – Friday: 7:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m.
Saturday by appointment only
Dignity Health Imaging Center, Prescott Valley
7700 East Florentine Road
Building B, Suite 105
Prescott Valley, AZ 86314
928.771.7577
Monday – Friday: 7:00 a.m. – 5:00 p.m.
Radiologists are medical doctors (MDs) or doctors of osteopathic medicine (DOs) who specialize in diagnosing and treating diseases and injuries using medical imaging techniques, such as x-rays, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET) and ultrasound. At YRMC, radiologists interpret the results of these studies and more, providing their expert diagnoses and recommendations to other physicians in order to help cure illness and heal injury.
Radiologists who specialize in diagnosing or treating diseases using “noninvasive” methods are called interventional radiologists. These physicians guide narrow tubes through the body’s arteries and organs with the help of x-rays and other radiologic equipment. Interventional radiologists deliver medications directly to an organ in the body, open blocked blood vessels, obtain biopsies and perform other procedures.
Accreditation by the ACR demonstrates excellence and commitment to exceptional radiologic services. The ACR awards accreditation to hospitals and other facilities that achieve high practice standards after a peer-review evaluation. Evaluations are conducted by board-certified radiologists and medical physicists who are experts in the field. According to the ACR, when you choose an ACR-accredited facility, you know that:
In order to make an appointment for an outpatient imaging study at YRMC East or YRMC West, you’ll need a referral from a licensed practitioner (e.g., physician, physician’s assistant, physical therapist or nurse practitioner). Once you have a referral, contact 928.771.7577.
Imaging Services has multiple locations, including:
Please bring your insurance information and other identification to your appointment.
Due to the type of studies conducted by Imaging Services, your family member or companion will need to wait for you in our comfortable lobby area. While they’re waiting, your family members are welcome to visit YRMC’s Cafeteria for meals, snacks and beverages. They also may want to stop by the YRMC Gift Shop.
YRMC’s radiologic technologists understand that children may be intimidated by the imaging equipment. That’s why we embrace Image Gently®, a radiation safety initiative that also addresses feelings children may have about imaging procedures. Our radiologic technologists are prepared to be especially reassuring to children. Parents and guardians are encouraged to check out YRMC’s Medical Radiation Safety brochure which features helpful information about medical imaging and safety for children.
Yes. Knowing that a patient is pregnant or could be pregnant is important information for all of your medical team, especially Imaging Services. Many imaging tests are not performed during pregnancy. However, while most medical x-rays do not pose a critical risk to a developing child, there may be a small likelihood of causing a serious illness or other complication. The actual risk depends on how far along the pregnancy is and on the type of x-ray. For example:
Talk to your doctor if you are breastfeeding. With your physician’s advice, you may decide to pump breast milk before the imaging exam and use it until after the contrast material clears your body, typically about 24 hours after the test.
Tell your physician about all medications – prescriptions, vitamins and herbals – you’re taking. Your doctor will advise you on what to do about the medications before your imaging study. Remember, it’s important to inform your physician of any recent illnesses or medical conditions before undergoing an imaging study.
There’s a slight risk of an allergic or adverse reaction with contrast materials. Because of this, it’s important that you tell your doctor about the following:
Our team will provide you specific instructions to help you prepare for your imaging study. Also, we are happy to answer any questions you might have. We’re here to help you!
Please wear loose, comfortable clothing. Depending on the type of imaging exam, you may be asked to remove some or all of your clothes and wear a gown during the exam. You may also be asked to remove, or leave at home, the following items:
You’ll receive diet instructions from your physician that will depend on the type of imaging exam you’re undergoing. If you have diabetes or other medical conditions it’s important that you inform your physician. In general, if you’re undergoing an exam that requires iodine or contrast material, you’ll be instructed to:
Most Imaging Services procedures are “minimally invasive,” meaning they are done without surgery. An advantage of this is that most interventional radiology procedures can be performed without anesthesia. Numbing medication may be used to minimize any pain around the procedure area. Often, patients also receive sedation medicine by IV to help them relax.
One of our experienced radiologists will analyze the images and provide your referring physician a report within 24-48 hours after the exam. Your physician will discuss the report as well as any follow-up examinations that are needed and why those follow-up studies are necessary.
Contact YRMC’s Health Information Management Department to get copies of your medical records.
Health Information Management
Dignity Health Yavapai Regional Medical Center – East
7700 East Florentine Road
Prescott Valley, Arizona 83614
Phone: 928.771.5657
Fax: 928.771.5785
Health Information Management
Dignity Health Yavapai Regional Medical Center – West
1003 Willow Creek Road
Prescott, Arizona 86301
Phone: 928.771.5657
Fax: 928.771.5785
YRMC’s Patient Financial Services can help you with questions regarding your bill.